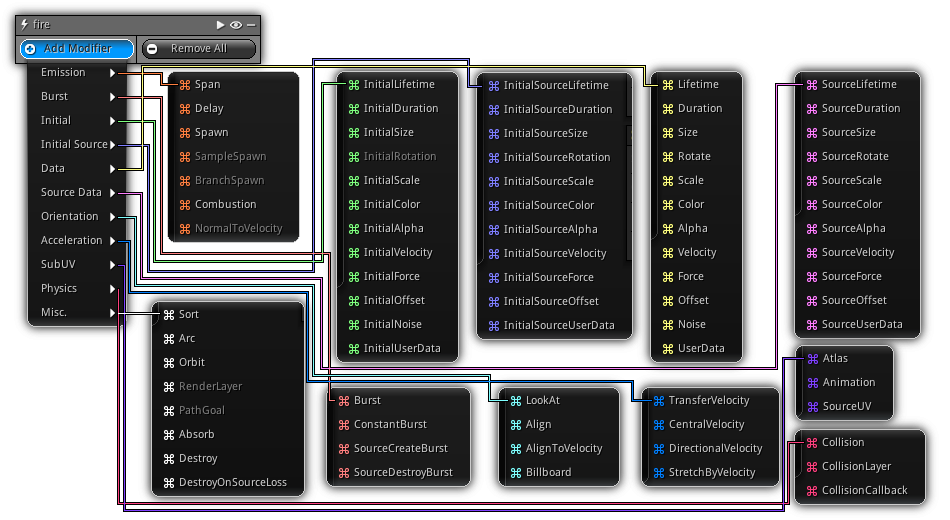
Particle modifiers not only dictate how particles will behave in space but also, control the way the particles are emitted. Take note depending on the type of emitter or the current state of the emitter, some modifiers might not be available or compatible. If it's the case they will appear grayed out and disable from the list or in the table itself and will be inactive (in case the emitter become incompatible with it).
Life Cycle
Before going more in depth with each particle modifier behaviors and properties it is important to firsts understand the life cycle of a particle to properly place modifiers. Each particle created will follow the cycle described below:
| Phase | Optional | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
Emission | Each frame the emitter will use the emission modifiers to try to create particles. The maximum amount of particles is controlled by the emitter itself. If a particle lifetime is set to 0 it means this particle is available for a new cycle. Within the particle modifiers list the Emission and Burst section contains all modifiers relevant for this phase. | ||
Initial | Occurs right after the emission. The system look to set the initial data on each particles looking for the entry located under Initial and Initial Source (if the emitter type is another emitter source. | ||
Update | The update phase is executed every frame for each particles that are still alive (lifetime > 0). During this phase particles data are modified on every tick; modifiers for this phase can be found under Data, Source Data, Acceleration, SubUV and Misc.. | ||
Physics | After the particle data have been updated and the final position of the particle is available to draw the current frame the system can run into the optional physics phase. If Physics modifiers are contained within the emitter modifier list this phase will detect if any particle that are still alive is colliding with the world. On collision callbacks can be triggered and detailed information about the collision is available to scripts and/or plugins. | ||
Draw | This phase finalize the transformation calculation for all particles, update the buffers and draw the particles on screen. It will be executed for each render layer drawing a particle system. The valid modifiers available for this phase are located in the Orientation and menu Misc.. | ||
Destroy | The particle duration is greater or equal to its lifetime; the particle goes back to standby waiting for a new life cycle to start. Take note modifier(s) can be added to the sequence to force a particle to be destroyed. Modifiers entry to force the destruction of particles can be found under the Burst and Misc.. section. |
- Warning
- The general workflow of a particle lifetime elaborated above is the generic version of the cycle. Some exception occurs, refer to each particle modifier description to learn on which phase they are effective.
Emission
Standard particle modifier to generate particles during the emission phase for regular emission types and emitters that depends on another source.
Span
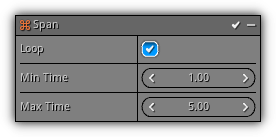
Add a cycle to the emitter. The cycle time of an emitter can be used by modifiers to determine if the value they should update should relative to the emitter cycle time or the emitter playback time.
Phase: Emission
Loop: Determine if the cycle should loop when the time limit is reached.
Min. Time: Minimum cycle time; 1.0 = 1 second. Max. Time: Maximum cycle time; 1.0 = 1 second.
- Note
- If the min. and max. values are different a random between the two will be generated.
Delay
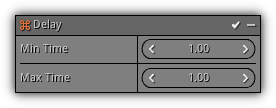
Delays the emission of particles and any subsequence cycles that are controlled by the Span modifier if any.
Phase: Emission
Min. Time: Minimum amount of time the emission phase should be delayed; 1.0 = 1 second. Max. Time: Maximum amount of time the emission phase should be delayed; 1.0 = 1 second.
- Note
- If the min. and max. values are different a random between the two will be generated.
Spawn
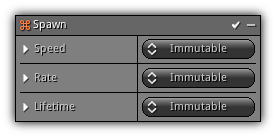
Probably the most common modifier that you will use to emit particles. This modifier is the generic interface to continuously create and launch particles in space. These types of modifiers generally launch particles over time based on a specific rate.
Phase: Emission
Speed: This value acts as a multiplier and should work in conjunction with the lifetime of the particle avoiding the emitter to overwork trying to find a particle that is ready for a new cycle. A value of 1 represents that in one second the emitter will generate Rate particles. With a value of 2, the emitter will generate Rate 2x per second etc...
Rate: How many particles should created per cycle.
Lifetime: The lifetime value to use for each new particle.
Sample Spawn
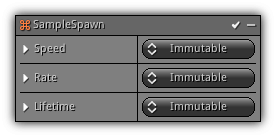
Very similar as the Spawn modifier but work on the emitter of the type Source. This modifier controls how many particles should be emitted for each source particle sample.
Phase: Emission
Speed: Controls how fast the emitter should look for new source particle to generate samples.
Rate: How many particles should be created for each source particle.
Lifetime: The lifetime value to use for each new particle.
Branch Spawn
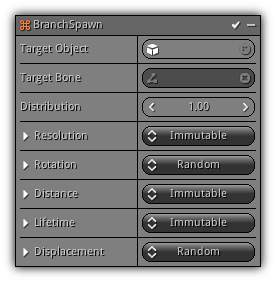
Valid for an emitter that uses the Source type; this emission modifier will emit in branches for each particle of the source emitter. It is ideal to create effects such as lighting or electricity.
Phase: Emission
Target Object: An optional object to calculate the direction of the branch. Instead, the particle emitter origin will be used to calculate the branching direction vector.
Target Bone: If the Target Object is a skeletal mesh on optional bone can be set to affect the direction of the branch samples.
Distribution: Factor that controls the percentage of samples that can be branched. A distribution value of 1.0 indicates that all source samples required branching, a value of 0.1 represent that only 10% of the samples required branching. This value will be randomly evaluated at emission time to decide which source particle will be branched.
Resolution: Control the amount of times the distance should be split creating a new branch.
Rotation: The amount of rotation that should be applied on the overall direction vector of the branching.
Distance: The maximum distance from the source particle towards the branching direction vector.
Lifetime: The amount of time the new particle can live.
Displacement: Optional offset that can be used to translate the new particles forward or backward in the branch direction.
Combustion
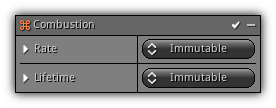
Emit particles using the active particle system object acceleration. Acceleration can either be controlled by animation curves, physics or manual user input using scripts or plugins. The larger the acceleration the more particles will be generated depending on the modifier rate (ie. 1m = Rate, 2m = Rate 2x etc...).
Rate: How many particles should per seconds while the emitter is moving. The acceleration of the object basically replaces the Speed parameter that can be found in other emission modifiers like Spawn.
Lifetime: The lifetime of each newly created particle(s).
Normal To Velocity

This modifier does not have any parameters; working only with an emitter that is using shape as an emission source. Using it will force the addition of the velocity data and will use the vertex normal of the geometry (if available) as velocity.
- Warning
- Place this modifier before any other emission modifier(s) present in the emission the sequence as it will send over the velocity data directly to modifiers that respond to the emission phase.
Burst
Section reserved for modifiers that emit a burst of particles at emission time.
Burst
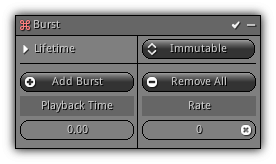
Default burst modifier to create a small "puff" of particles using a predefined playback time(s). Take note this modifier is compatible with the Span modifier allowing you to loop the burst cycles.
Phase: Emission
Lifetime: Value that specifies the lifetime of each particle that occur during the burst.
Add Burst: Add a new burst entry.
Remove All: Remove all existing burst entry to restart fresh.
Playback Time: The emitter playback time when the burst should occur.
Rate: How many particles should be created.
To remove a specific entry click its ![]() icon to cancel the burst rate for the selected playback time.
icon to cancel the burst rate for the selected playback time.
Constant Burst
Constantly emits a burst of particles.
Phase: Emission
Rate: How many particles should be created per burst.
Lifetime: How long each particle generated by the burst will live.
Source Create Burst
Available when the emission type is set to Source, this modifier will generate a burst every time a new source particle is created.
Phase: Emission
Rate: How many particles should be created per burst.
Lifetime: How long each particle generated by the burst will live.
Source Destroy Burst
Available when the emission type is set to Source, this modifier will generate a burst of particles for each source particle that gets destroyed.
Phase: Emission
Rate: How many particles should be created per burst.
Lifetime: How long each particle generated by the burst will live.
Initial
The type of particle modifiers found in this submenu is used to set the initial value of particle data.
Initial Lifetime
Phase: Initial
Controls the initial lifetime value of the particle.
Initial Duration
Phase: Initial
Controls the initial duration of the particle. The duration represents the actual time a particle has been living; it is not to be confused with lifetime which represents the maximum amount of time a particle can live. When the duration of a particle reaches its max. lifetime value, it will die. Many modifiers use the relation duration vs lifetime and use this relative ratio to interpolate values etc...
Initial Size
Phase: Initial
Controls the initial size of the particles on the X and Y axis before transformation an additional transformation is applied.
Initial Rotation
Phase: Initial
Specify the initial XYZ rotation of the particle. Only available when the type of particle is set to Sprite (a tri-dimensional quad).
Initial Scale
Phase: Initial
Controls the initial scale of the particle on the XYZ axis. Not to be confused with the Size data; the scale occurs later in the particle transformation calculation and act as a multiplier to the size on all axis (when applicable).
Initial Color
Phase: Initial
The initial RGB value of the particle.
Layer Index: Specify on which color layer the specified color should be applied. Each particle can have up to 4 color layer that can be used by your shaders.
Initial Alpha
Phase: Initial
The initial alpha value of the particle.
Layer Index: Specify on which color layer the specified alpha value should be applied.
Initial Velocity
Phase: Initial
Set the initial velocity value of the particle; control how fast and in which direction the particle will be moving.
Initial Force
Phase: Initial
Set the initial force value for the particle. Not to be confused with velocity; the force is a value to represent something like gravity or wind either pushing or pulling a particle. Velocity and force are working in conjunction.
Initial Offset
Phase: Initial
Translate the initial particle location by adding an offset on the XYZ axis.
Initial Noise
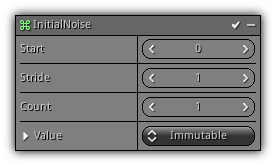
Phase: Initial
Add noise to the initial particle position based on their index.
Start: The particle index to begin with.
Stride: The step size.
Count: The maximum amount of particles affected by the noise.
Initial UserData
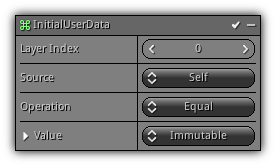
Phase: Initial
To give more flexibility another data type is available; the user data type, it contains up to 4 layers and can be used to store any type of information using a vector. The data can be assigned in any way you see fit and is available and a standard source data to all operations. This modifier provides a way to set up user data during the initial phase.
Layer Index: Select on which layer you want the data to be stored.
Initial Source
Available only when the emission type of the emitter is set to Source. These initial modifiers allow you to get direct access to the active particle source data to affect its properties. By default, all source data point to the same data the modifier is associated with.
Initial Source Lifetime
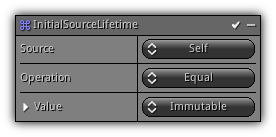
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial lifetime using of the referenced particle data.
Initial Source Duration
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial duration using of the referenced particle data.
Initial Source Size

Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial size using of the referenced particle data.
Initial Source Rotation
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial rotation using of the referenced particle data.
Initial Source Scale
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial scale using of the referenced particle data.
Initial Source Color
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial color using of the referenced particle data.
Layer Index: The color layer used to store the color data.
Initial Source Alpha
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial alpha using of the referenced particle data.
Layer Index: The color layer used to store the alpha data.
Initial Source Velocity
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial velocity using of the referenced particle data.
Initial Source Force
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial force using of the referenced particle data.
Initial Source Offset
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial offset using of the referenced particle data.
Initial Source Userdata
Phase: Initial
Set the active particle initial user data using of the referenced particle data.
Layer Index: The user data layer index used to store the vector value.
Data
Access and modify a specific particle data during emitter playback.
Lifetime
Phase: Update
Update the particle lifetime data.
Duration
Phase: Update
Update the particle duration data.
Size
Phase: Update
Update the particle size data.
Rotate
Phase: Update
Update the particle rotation data.
Scale
Phase: Update
Update the particle scale data.
Color
Phase: Update
Update the particle color data.
Layer Index: Specify on which color layer the data should be affected.
Alpha
Phase: Update
Update the particle alpha value.
Layer Index: Specify on which color layer the data should be affected.
Velocity
Phase: Update
Update the particle velocity data.
Force
Phase: Update
Update the particle force data.
Offset
Phase: Update
Update the particle offset data.
Noise
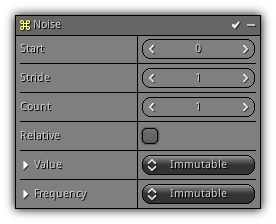
Phase: Update
Update the particle noise data.
Start: The particle index to begin with.
Stride: The step size.
Count: The maximum amount of particles affected by the noise.
Value: Distribution that controls how much noise value should be applied.
Frequency: Controls how fast (in Hz) a new noise value should be calculated and affected to a particle within the noise range.
Userdata
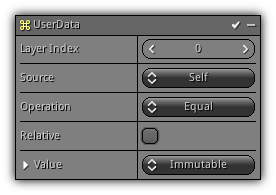
Phase: Update
Update the particle user data.
Layer Index: Specify on which user data layer the vector should be affected.
Source Data
These modifiers are available when the emission type of the emitter is set to Source. Using the modifier from this menu gives direct access to the active particle source data to affect its local properties during its update phase.
Source Lifetime
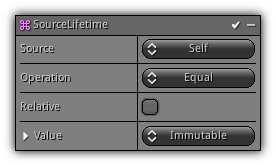
Phase: Update
Update the particle lifetime using the source particle data.
Source Duration
Phase: Update
Update the particle duration using the source particle data.
Source Size
Phase: Update
Update the particle size using the source particle data.
Source Rotate
Phase: Update
Update the particle rotation using the source particle data.
Source Scale
Phase: Update
Update the particle scale using the source particle data.
Source Color
Phase: Update
Update the particle color using the source particle data.
Layer Index: Select the color layer to update.
Source Alpha
Phase: Update
Update the particle alpha using the source particle data.
Layer Index: Select the color layer to update.
Source Velocity
Phase: Update
Update the particle velocity using the source particle data.
Source Force
Phase: Update
Update the particle force using the source particle data.
Source Offset
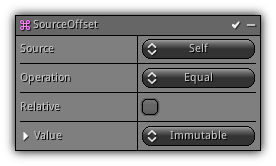
Phase: Update
Update the particle offset using the source particle data.
Source Userdata
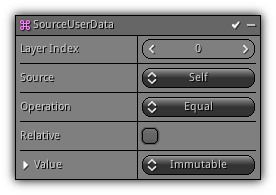
Phase: Update
Update the particle user data using the source particle data.
Layer Index: Specify the user data layer to update.
Orientation
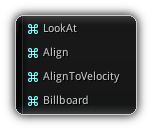
This section contains modifiers that directly affect the final rotation of the particles.
Lookat

Phase: Draw
Force each particle orientation to point to the active render layer camera the particle system draws on.
Align

Phase: Draw
Use a custom direction vector to force each particle orientation to look towards it.
Align To Velocity

Phase: Draw
Use the particle velocity vector to align the orientation of the particle.
Billboard

Phase: Draw
Force all particles to be aligned to a specific world axis.
Acceleration
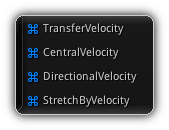
Helper modifiers to deal with particle velocity data during the initial and update phase.
Transfer Velocity

Phase: Initial
Use the active particle system acceleration to initialize the velocity of the particles.
Central Velocity
Phase: Initial
Use the particle emitter pivot point and the initial particle position to calculate a direction vector that will be affected by the velocity of the particle.
Directional Velocity

Phase: Initial
Rotate the default up axis (+Z) by the emitter transformation to calculate the particle velocity direction.
Stretch By Velocity
Phase: Update
Adjust the particle sizes depending on their active velocity.
Min. Clamp XYZ: The minimum value to clamp the size on each axis.
Max. Clamp XYZ: The maximum value to clamp the size on each axis.
Factor: The velocity factor to used to increase/decrease the size of the particles.
SubUV
Helpers to control the texture UV data of the particles.
Atlas
Phase: Initial
Use a texture atlas to select the texture coordinate that should be used by the new particle.
Layer Index: Specify which texture coordinate layer the modifier should use.
Randomize: If turned on; do not use the Cell Index distribution and choose a random cell from the atlas grid.
Width: The width of the texture atlas in pixels.
Height The height of the texture atlas in pixels.
Cell Width: The width of the cell in pixels.
Cell Height: The height of the cell in pixels.
Cell Index: The cell index to use.
Animation
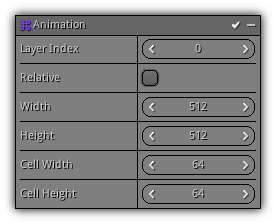
Phase: Initial & Update
Use a texture atlas to progressively change the particles texture coordinate creating an animation sequence.
Layer Index: Specify which texture coordinate layer the modifier should use.
Relative: Progressively select a cell based on the life span of the particle.
Width: The width of the texture atlas in pixels.
Height The height of the texture atlas in pixels.
Cell Width: The width of the cell in pixels.
Cell Height: The height of the cell in pixels.
Source UV
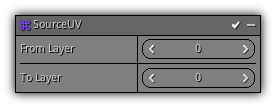
Phase: Update
Copy the texture coordinate from the source particle to the active particle.
From Layer: The texture coordinate layer to use for the source.
To Layer: The texture coordinate layer to use for the destination.
Physics
Controls particles collision with the physics world.
Collision
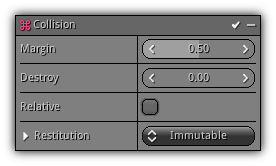
Phase: Update
Enable particle collision.
Margin: The collision margin of the particle pivot point.
Destroy: This parameter controls the percentage of particles that should be destroyed automatically. Since particles collision is computationally expensive the modifier provided you a Russian roulette like mechanism to destroy particles using a random factor. Specifying a value of 0.1 tells the system that there is a 10% chance that the particles get destroyed. Using this mechanism you have more control over the ratio of particles that is ray traced with the physics world.
Restitution: Controls how much absorption should be applied on the particle when it actually hit something.
Steps: The number of sub-steps used to discover a hit depending on their collision margin. The steps act as a forward multiplier as it increases the velocity vector n times the margin value to find a potential hit.
- Warning
- The collision modifier adds quick (and dirty) collision on a particle basis. It should only be used by the emitter(s) that does not have a massive amount of particles( ie. to create bouncing sparks etc...). For massive emitters, it is recommended to use entities that contains actual physic object and bounds (as collision will run in parallel to the main thread; and will use bounds to bounds acceleration schemes) and use (ie) a transform modifier to face the camera.
Collision Layer
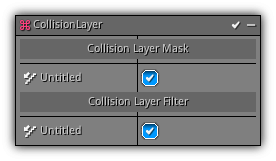
Phase: Update
By default, when adding the Collision modifier that particles will interact will all collision layers. This modifier allows you to control which collision layer the particles can collide with.
Collision Layer Mask: The collision layer(s) where the particles belongs to.
Collision Layer Filter: The collision layer(s) the particles can collide with.
- Warning
- In order for this modifier to work properly, it must be placed before the
Collisionmodifier since the data will be passed to the modifier function during the update phase.
Collision Callback

Phase: Update
Force the system to trigger an OnContact callback every time a particle collides with something in the physics world. More detailed information about the collision will be sent to the script or plugin callback function.
- Note
- Particles are cannot collide with themselves they can only collide with other physics object(s) that are present in the world.
- Warning
- In order for this modifier to work properly, it must be placed before the
Collisionmodifier; same as the Collision Layer modifier.
Misc.
Miscellaneous particle modifiers to control different properties and behavior at update time.
Sort

Phase: Update
Quickly sort particles using their actual distance with the active render layer camera.
Arc
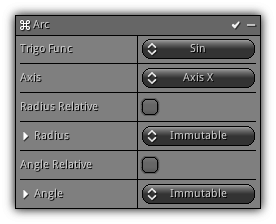
Phase: Initial & Update
Add extra translation to the particle using trigonometric functions allowing you to create arcs, sphere, swirl, torus and a lot more. Works best when the angle parameter is relative and combined with other Arc modifiers.
Trigo Func: The trigonometric function to use.
Axis: The axis to operate on.
Radius: The distance or magnitude of the Trigo. function operation if you prefer.
Angle: The angle in degrees to pass to the Trigo. function.
Orbit
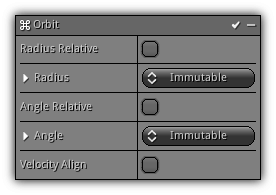
Phase: Initial & Update
Make particles orbit and tumble (velocity align) around their emission point applying sin/cos on the X and Y axis.
Radius: The distance from the emission point.
Angle: Angle in degrees to use for as the orbit rotation.
Velocity Align: Force the particles to be aligned to their velocity adding a tumble effect to the orbit.
- Warning
- Adding the
Orbitmodifier will not add velocity data to the particles since theVelocity Alignparameter is optional to the orbit operation.
Render Layer
Phase: Initial
Specify on which render layer the new Matter (see Particles for more info.) should be placed on.
Render Layer: Creates the render layer mask that will be applied on the new entity created during the Initial phase.
Path Goal
Phase: Initial & Update
Available when the particle emission is set to Wire this modifier gives you the ability to set a goal in 3d space for the wire to reach.
Target Object: The target object to use for the path.
Target Bone: If the Target Object is a skeletal mesh you can specify an optional bone to use as the final target.
- Remarks
- To restart the goal interpolation use a
Spanmodifier; to prevent particles to go beyond the goal position use theAbsorbmodifier. In addition, the modifier only set the start point and the end point (in the time range between 0 to 1); you can tweak curves on each axis by adding additional points.
Absorb
Phase: Initial & Update
Destroy a particle if it reaches a specific distance with a point in 3d space.
Target Object: The object to use as to target.
Target Bone: If the Target Object is a skeletal mesh this field allow you to specify a bone to use as the target.
Threshold: The minimum distance from the target that the particle can reach before being destroyed.
Destroy
Phase: Update
Force a particle to be destroyed using a custom condition defined by the user.
Axis Type: Choose the axis to evaluate or use the magnitude of the source to determine if the particle should be destroyed.
Func: The logical operator function to used to evaluate the condition.
Destroy On Source Loss
Phase: Update
Available when the emission type is set to Source; this modifier force the particles to be destroyed if the source particle it references to died.
|
|
